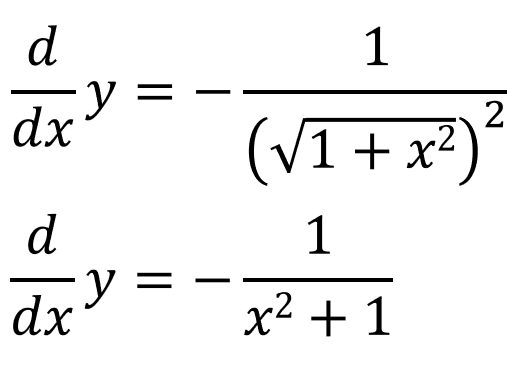First lets start with a right-angled triangle where one of the angles is y. Lets say the opposite side is of length 1 and that the adjacent is of length x:
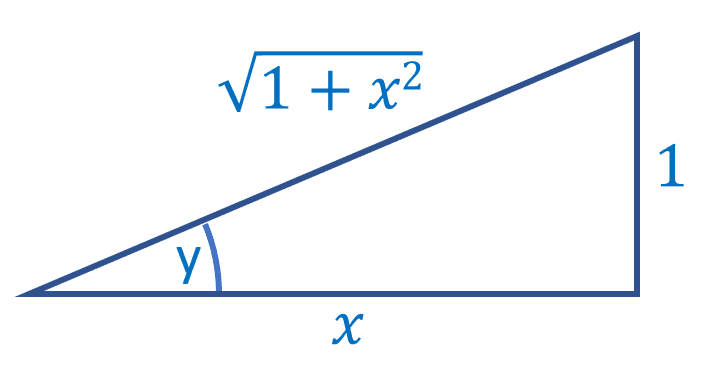
Using the triangle above, we can say:
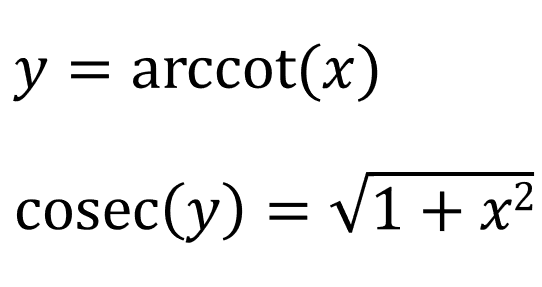
We already know that the derivative of x with respect to x is 1:
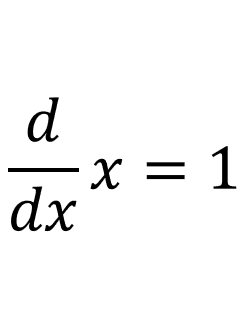
Since x = cotan(y):
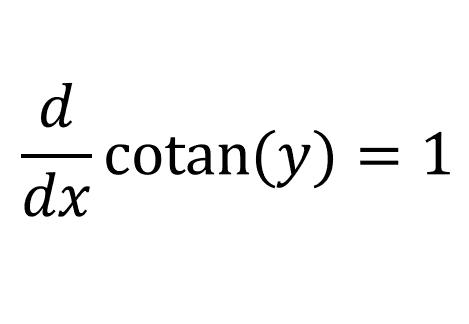
Using the chain rule:
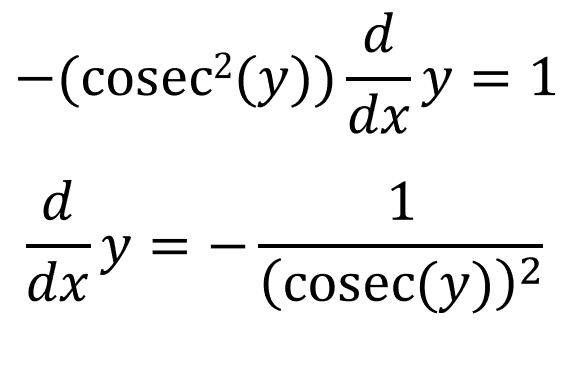
And we already know what cosec(y) is equal to: